Crowd Sourcing and Community Detection
Guide: Prof. V.S. Borkar, IIT Bombay
CrowdsourcingCrowdsourcing is the process of obtaining needed services (data labelling, user ratings) from a large group of people, especially from an online community. Small tasks, like labelling data, are allotted to humans - termed as workers - who are then paid for completing these. The collected data can then be used of training machine learning systems.
Challenges in crowdsourcing and their proposed solutions are explored in this literature review. Application of matrix factorization methods in task routing and label aggregation, adaptive task assignment were studied. An interesting paper outlined a modification of Adaboost algorithm for detecting non-linear classifiers, using humans as basic classifier.
Community DetectionIt happens many a times that a group decides to give the same rating to a movie, or close followers of a celebrity are strongly influenced by their views about an issue. We proposed an algorithm to find out communities like these in a social network.
We are given the graph and the binary rating given by all the nodes to a particular topic (eg. a movie). The vector of ratings is recursively multiplied by the transition probability matrix and then thresholded. The nodes corresponding to high value in the thresholded vector belong to the said community. The algorithm was tested on various synthetic and real world datasets and showed good results for networks that have a structure similar to social networks
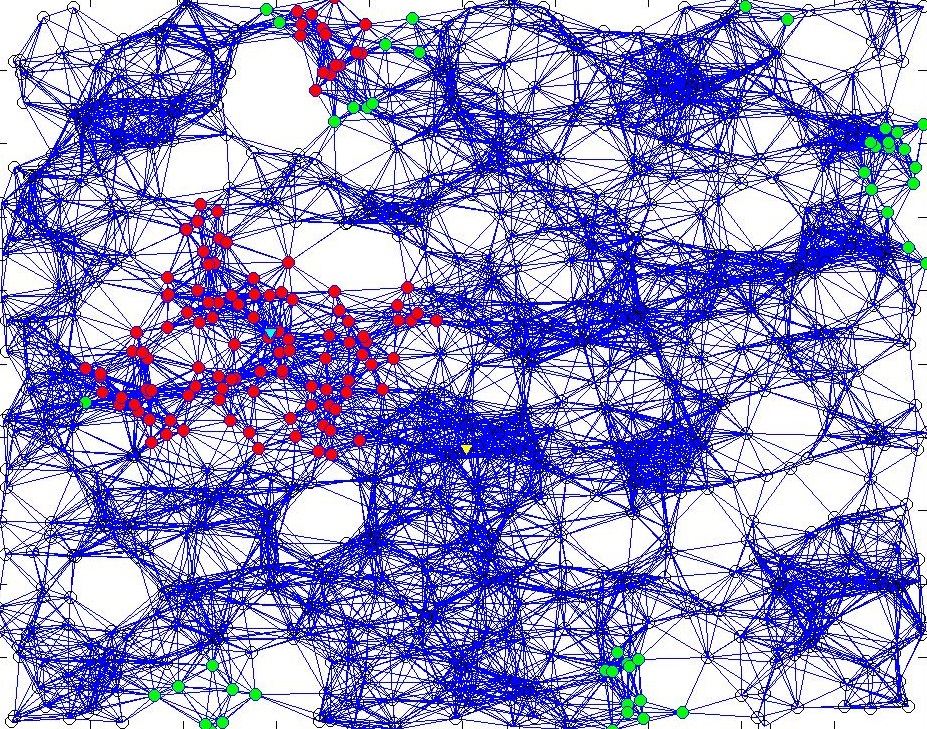
Fig1: A geomteric graph with 1000 nodes. Shown in green are the nodes that gave rating of 1. The community detected after running the algorithm on this has been shown in red. A large community has been detected around a cyan node (influential node). Another small community has been wrongly detected.